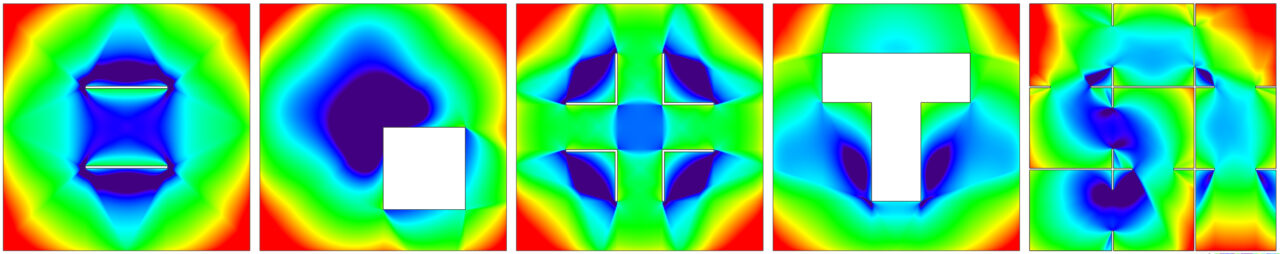
Skewness (Sv) expresses the mean of the cube of deviation between all radial lengths and average radial length of an isovist (Benediky, 1979). In visibility graph terminology, it represents the point third moment for a location. When Skewness is positive, long radials are few in number and short radials many; when it is negative, the opposite is the case. Cave interiors have positive Skewness; space near columns, trees or outside corners have negative Skewness. The latter might correlate with a sense of exposure, the former with safety or power.
To determine Skewness, the Isovist_App calculates the average distance between each edge of the polygon of the isovist, and the origin point of the isovist calculated at V. It then finds the cube of the difference between the latter and Average Radial (Qv). It subsequently calculates the mean of all such values, as weighted by the arc angle associated to each edge. The final outcome is cube rooted.
In notation form the calculation for Skewness is expressed as:
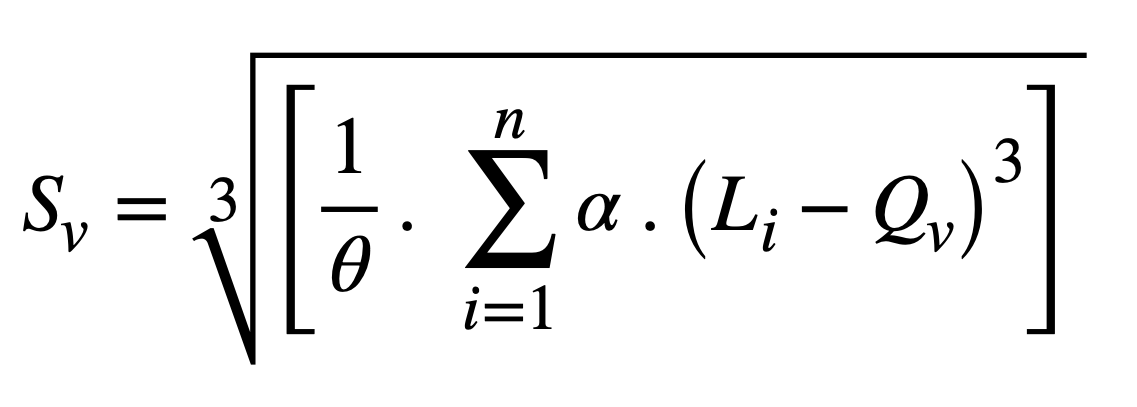
Where Li is is average length to each edge of the isovist polygon, Qv the average radial value, n the total number of edges of the isovist, alpha the angle subtended by each edge, and theta the total sweep of the isovist.